Detailed Product Evaluations
A major objective of SPoRT is to not "throw data over the fence." SPoRT focuses on researching products to address operational needs, transitioning these products to operational users, and then evaluating the effectiveness of these products. These evaluations take the form of online surveys and intensive survey periods where our partner National Weather Service Offices make a concerted effort to provide feedback for a given period of time. These surveys and evaluations are then gathered together to create reports for journal articles, conference papers, or the Science Advisory Committee. This page provides a review of several specific events and evaluation periods.
EVALUATION

Impact of GPM Level 2 (Passive Microwave) and Level 3 (IMERG) Rain Rates on WFO and RFC operations: Trial Period Summer 2015
NASA-SPoRT conducted a trial evaluation of SPoRT's Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission products - beginning July 15, 2015 and ending August 30, 2015. It was performed in collaboration with WFOs and RFCs in three regions: Alaska (Anchorage, Juneau and Alaska/Pacific RFC), Southwest U.S. (Albuquerque, Tucson, Colorado Basin RFC), and Southeast U.S. (Peachtree City, Southeast RFC). Level 2 passive microwave swath data provides ~2 hour latency, frequent overpass estimates of rain rate from ~10 satellites. Level 3 Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) provides ~6 hour latency 0.1° gridded (near-)global calibrated rain rate estimates, as well as accumulated rainfall totals for 1-, 3-, 6-, 12-, and 24-hr periods. Despite the latencies, forecasters in radar-weak and data-void regions made good use of the products. This report summarizes the results of the trial. View the report.
EVALUATION

Impact of the 24-hour Microphysics RGB Imagery for Alaska Aviation Forecasts of Low Clouds during Summer 2015
An assessment was conducted from June 15 to August 7 by NASA/SPoRT in collaboration with operational forecasters in Alaska WFOs regarding the use of multi-spectral (i.e. RGB) imagery from VIIRS (NPP) and MODIS (Aqua & Terra) as a proxy to future JPSS and GOES satellite missions for the purpose of improving analysis of low ceiling and visibility hazards to aviation users for use in nowcasts/forecasts (i.e. TAFs). The 24-hr Microphysics RGB is very similar to the Nighttime Microphysics RGB except the green component uses the 11-8.7 μm channel difference vs the 11-3.9 μm channel difference and therefore, the 24-hr Microphysics can be used at all times of day. User feedback, application examples and recommendations are presented. View the report.
EVALUATION

GOES-R CI Proxy for Aviation: Trial Period 2015
NASA-SPoRT conducted a trial evaluation of the operational utility of the GOES-R Convective Initiation proxy product (GOES-R CI) at specific NWS weather forecast offices (WFOs) and Center Weather Service Units (CWSUs) during June and July of 2015. The GOES-R CI product can be used as a proxy to the future capabilities from GOES-R which will have improved spatial and temporal resolution that are anticipated to benefit the GOES-R CI performance. In this evaluation, the NWS WFOs and CWSUs evaluated the impact of the GOES-R CI proxy product to provide situational awareness for aviation support during the summer season of difficult-to-predict "pop-up" convection near airports and along flight paths. The report contains user examples and recommendations. View the report.
EVALUATION

SPoRT-LIS
The SPoRT-LIS was assessed by the NWS forecast offices at Huntsville, Houston, and Raleigh to determine its utility for drought monitoring and assessing areal flooding potential. The final report summarizes the use of the SPoRT-LIS soil moisture output fields during the August to October 2014 assessment period, highlighting how the product was applied during weekly contributions to the U.S. Drought Monitor and used during potential flooding situations. View the report.
EVALUATION
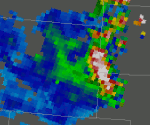
NESDIS Snowfall Rate Product
This report summarizes the Winter 2014 assessment of a passive microwave snowfall rate (SFR) product developed by NOAA/NESDIS/STAR. NWS forecasters provided feedback via online surveys or blog posts after viewing these data in their native display system for relevant snowfall events. Traditionally, radar and satellite visible and IR imagery has been used to detect snowfall, but the SFR product allows for detection of snow in cases when radar coverage is limited or mixed precipitation is present. View the report.
EVALUATION

Aviation and Cloud Analysis using RGB Imagery by High-Latitude Forecasters
Products evaluated include the Day-Night Band (DNB) Red, Green, Blue (RGB) composite imagery, the Nighttime Microphysics (NtMicro) RGB, and the SPoRT Hybrid GEO/LEO 11-3.9µm product. The assessment sought to determine the value added to the short-term forecast of ceiling and visibility, particularly as they apply to TAFs issued by high-latitude WFOs. In addition, the assessment exposed forecasters to the application of complex multi-spectral imagery (i.e. RGB composite), and hence, the future paradigm of satellite imagery that will become available in the JPSS and GOES-R eras. View the report.
EVALUATION

VIIRS Front Range Nighttime Imagery
This report describes the 2013/14 assessment of multi-spectral imagery produced by the NASA Short-term Prediction Research and Transition (SPoRT) Program from the MODIS and VIIRS polar-orbiting instruments for application by its Weather Forecast Office (WFO) collaborators within the NWS Southern and Eastern Regions. NWS forecasters provided feedback via online surveys or blog posts after viewing data within their native display system for a relevant event where products were used to support aviation hazards and cloud analysis. GOES 11-3.9µm difference imagery has traditionally been used to analyze and track low clouds and fog at night to support the preparation and amendment of TAFs. The DNB and NTmicro RGB products provide additional information within a single image to increase the forecaster's awareness of cloud characteristics that apply to aviation hazards.
EVALUATION

Aviation and Cloud Analysis using RGB Imagery by Southern Region WFOs
This report summarizes the assessment of a suite of Suomi-National Polar-orbiting Partnership (S-NPP) Visible Infrared Imager Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) products to address the detection of dust, smoke, clouds, and other obstructions to visibility at night. The assessment was conducted during July and August 2013 and used a combination of single channel and red-green-blue (RGB) composite product VIIRS imagery, which are described in detail in the products description section. The assessment included the participation of four National Weather Service (NWS) Weather Forecast Offices (WFOs) spanning three NWS regions. The offices included Albuquerque, New Mexico (Southern Region), Boulder, Colorado and Cheyenne, Wyoming (Central Region), and Great Falls, Montana (Western Region). Collectively, these four offices are part of the Front Range collaboration.
EVALUATION

GOES-R Convective Initiation Product
GOES-R Convective Initiation (CI), developed by UAH, is a satellite-based nowcasting (0-2hr) product that fuses geostationary satellite data and numerical weather prediction model output to produce a probability of CI, where CI is defined as a 35+ dbz radar echo. It can provide leadtime ahead of ground-based radar and can provide insight into the environment by indicating trends in cloud growth. Cloud objects are first identified by type, and growing cumulus clouds are tracked over consecutive satellite scans.
- GOES-R Convective Initiation Product Assessment
- This assessment report describes the GOES-R CI assessment that took place from September 1 to October 31, 2013 among the Albuquerque, Corpus Christi, Huntsville, and Miami WFOs. The CI product is a proxy to the future capabilities of the Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) on GOES-R. The previous version used a "Strength of Signal" styled product based on satellite-only indicators and temporal trends. The new version utilizes numerical weather prediction data to characterize the convective environment and it continues to utilize current GOES infrared channels to measure cloud growth rates, cloud depths, and cloud ice or water path to produce a probabilistic value of CI. The purpose of this assessment is to better understand the value of the additional model data and the change to a probabilistic-based product to the product utility, and to evaluate the use of GOES-West data within the current version of the algorithm for the first time in operations.
EVALUATION

MODIS False Color Snow Detection Product
SPoRT provides the MODIS False Color composite to our WFO partners where snow cover is a forecast concern. This product combines one visible channel with two shortwave infrared channels to highlight features with infrared signatures. The advantage of this product is that snow is spectrally different from clouds and clear ground at wavelengths greater than 1.4 microns. This difference is enhanced with colors to enhance the locations of snow (red), clouds (white) and clear ground (green).
- Great Falls Evaluation 2008
- This paper describes the MODIS False Color product in detail, outlines the collaboration that has taken place between WFO Great Falls and SPoRT, and describes how the product is used operationally. An assessment period from January to March 2008 yielded two case examples, presented here. This paper emphasizes the impact the false color product has in the WFO’s hydrologic situational awareness and how this information can be used to influence operational decisions. In general, the product has show value throughout the forecast process and compliments other data sets and products from agencies such as NOAA/NOHRSC (see associated link to poster).
- Great Falls Evaluation 2008 - Poster
- Evaluation of the MODIS False Color product culminated in this poster presented at the 2009 AMS annual meeting. The poster provides an excellent opportunity to quickly communicate the product's function and impact, and could serve as a quick introductory training piece or a seasonal refresher. Comparison images show how it improves on standard imagery, and a time series of images is presented for a large snow event and melt during 2004. Note the center of the poster where a diagram shows how the MODIS False Color product has ties to improve each phase of the forecast process.
EVALUATION

MODIS Spectral Difference (Fog) Product
Another MODIS product provided by SPoRT to our WFO partners is the Spectral Difference or Thermal Difference product. This is more commonly referred to as the MODIS Fog product. This product takes advantage of the lower thermal emissivity of water clouds (3.9 micron) versus land surfaces (11 microns). This difference, calculated during the pre-dawn hours is compared to a threshold value to highlight regions of fog (yellow) versus high clouds (blue). Care must be taken as this is valid only at night and multi-layered stratus clouds may give a false indication of fog, when fog is not present.
- Albuquerque MODIS Evaluation (Jan. 2009)
- The Albuquerque, NM WFO is not the “fog” capital of the U.S., but this case example is an excellent example of how NASA polar-orbiting satellite data can help enhance the use of geostationary imagery. The MODIS spectral difference product (i.e. Fog/Low Cloud product) at 1km resolution can detect fog in narrow valleys or during events of thin fog where GOES is sometimes limited. The use of the MODIS Fog product by forecasters is demonstrated here with several comparison images as well as TAF and observational data..
EVALUATION

Total Lightning Products
The North Alabama Lightning Mapping array (NALMA) data are provided by SPoRT to four of our partner WFOs. These include Morristown and Nashville, Tennessee as well as Birmingham and Huntsville, Alabama. Additionally, The Sterling, Virginia office receives data from the Washington D.C. network (DCLMA). These networks provide information on total lightning, that is both intra-cloud and cloud-to-ground observations. This ability to observe the intra-cloud component has been used by SPoRT's WFO partners to enhance their situational awareness as well as their warning decision support operations.
- Operational NALMA Uses with WFO Huntsville
- This is the paper presented at the 2009 AMS Conference in Phoenix, AZ. This paper serves as the basis for an upcoming BAMS Maproom article. This overview discusses how the NALMA data have been used to support both situational awareness and the warning decision support process for the NWS Huntsville office. Three cases discussed range from the "Super Tuesday" outbreak that resulted in two EF-4s in the Huntsville county warning area (6 Feb 2008), a large hail event on 2 Aug 2008, as well as a squall line event where the NALMA were used to highlight the locations where cloud-to- ground lightning activity may begin (31 May 2004). Additionally, SPoRT's role in training and assessments are discussed and the future role of the Geostationary Lightning Mapper.
EVALUATION

GOES Aviation and MODIS Fog Products
SPoRT has partnered with NESDIS to evaluate several GOES fog products in conjunction with NASA's MODIS spectral difference product. SPoRT has conducted two intensive evaluation periods, with the most recent occurring from 5-25 January 2009.
- August 2008 and January 2009 Evaluation
- This is a preliminary summary of the intensive evaluation period focusing on the GOES Aviation products. These include the Low Cloud Base and Fog Depth products. This evaluation period was conducted with SPoRT's partner NWS offices from August 2008 (inland) and January 2009 (coastal and southwest U.S.).

